0
-
An empty cart
You have no item in your shopping cart
envato-wordpress-toolkit domain was triggered too early. This is usually an indicator for some code in the plugin or theme running too early. Translations should be loaded at the init action or later. Please see Debugging in WordPress for more information. (This message was added in version 6.7.0.) in /var/www/wp-includes/functions.php on line 6121g5plus-darna domain was triggered too early. This is usually an indicator for some code in the plugin or theme running too early. Translations should be loaded at the init action or later. Please see Debugging in WordPress for more information. (This message was added in version 6.7.0.) in /var/www/wp-includes/functions.php on line 6121The last few parts of this Section (3J to 3M) have been concerned almost entirely with the clarification of a flow of fluid, usually to remove contaminants from it, and very often in a utility function. Most of the remaining parts are now concerned with process filtration, in which the filtration process is intended to recover valuable solids from suspension in a liquid.
Leaf and plate filters are mostly relatively simple pressure-driven filters made up of flat filtration elements, although they can also be vacuum driven. The overall configuration of the filter may be horizontal or vertical, and the basic choice
between them is often made according to the space available in the factory. They are mainly used for batch-operated solids recovery, although in combination with pre-coat they can also be employed for clarification and decontamination duties.
In leaf filters, the elements hang from a manifold at their top, are square, rectangular or circular in shape, and have filter media on both sides. Plate filters have their array of, usually circular, elements mounted one above the other on a central
support, and usually filter only on the top surface. Some different leaf and plate elements are illustrated in Figure 3.61. Some care is necessary over the use of words to describe the orientation of the elements in these filters. In this book, horizontal plate
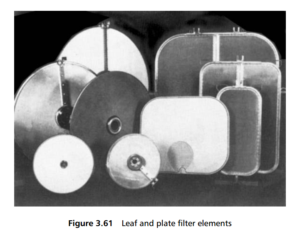
filters have the plates mounted on a vertical support, but the plates are horizontal around it (and the pressure shell containing the array of elements is also a vertical cylinder). Leaf filters are vertical element filters, mounted on a horizontal support in a horizontally oriented pressure vessel.