0
-
An empty cart
You have no item in your shopping cart
envato-wordpress-toolkit domain was triggered too early. This is usually an indicator for some code in the plugin or theme running too early. Translations should be loaded at the init action or later. Please see Debugging in WordPress for more information. (This message was added in version 6.7.0.) in /var/www/wp-includes/functions.php on line 6121g5plus-darna domain was triggered too early. This is usually an indicator for some code in the plugin or theme running too early. Translations should be loaded at the init action or later. Please see Debugging in WordPress for more information. (This message was added in version 6.7.0.) in /var/www/wp-includes/functions.php on line 6121Conventional downflow sand filters are effective for liquid-solid separation at flow rates up to about 15m3/h.m2 of filter area, although higher rate downflow filters are available. With proper selection of filter media, gelatinous as well as granular suspended matter can be filtered out, without a rapid differential pressure build-up.
The bed is cleaned by a reverse, upward flow of filtrate water, sufficient to expand and fluidize the granules of the bed. When sufficient backwash liquid has passed through the bed, the bed particles settle back into place under the influence of gravity. If the particles are all of the same material, then the largest ones will settle at the bottom of the bed and the smallest ones at the top, which is the wrong way round as far as filtration is concerned, which is best achieved under downflow conditions by having the largest pores (created by the largest particles) at the top of the bed, first meeting the incoming raw water.
Typical filter media for the downflow filter consist of selected silica sands, and coal or anthracite, which are tough inert solids, available in a range of particle sizes. One solution to the problem of matching the pore sizes in the bed is to use layers of different solids, with different densities. If the denser material also has the smallest particle size, then the layers will resettle after backwashing with the finest at the bottom and the coarsest on top. The effect in a two-layer bed is shown
in Figure 4.1, where the trapped solid concentrations are plotted for a conventional bed as well.
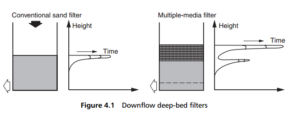
Materials for use in multi-layer downflow beds include anthracite, with a specific gravity of 1.4, flint sand (2.65) and garnet (3.83). Magnetite (4.9) can be used for a fourth layer if necessary.
A two-stage multi-media filtering system, shown in Figure 4.2 has been developed to treat turbid surface waters coming from rivers, lakes, reservoirs or the sea, but which are low in colour, iron and manganese. Whilst operational, oxidizing and coagulant solutions are injected into the primary (upper) vessel, and a further coagulant is also injected prior to the second (lower) vessel. The primary filter
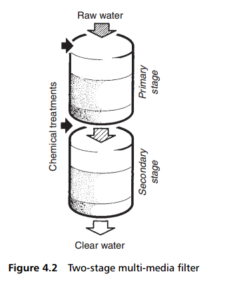
medium comprises anthracite, supported by a layer of silica sand. The secondary filter medium comprises a medium-sized layer of silica sand, supported by the final polishing layer of garnet or barium sulphate. The system has four programmable
self-cleaning steps, using the normal backwash principle.